Chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, and obesity are becoming increasingly common worldwide, largely due to lifestyle factors. These long-term health issues not only affect daily life but also place a heavy burden on healthcare systems. Managing them effectively requires more than just medication—it demands lifestyle changes, particularly in physical activity. This is where Exercise Physiology plays a crucial role. Exercise physiology is the science of how the body responds to movement and exercise. With the guidance of trained professionals, safe and tailored exercise programs can improve health outcomes, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life. This blog explores how exercise physiology supports chronic condition management using practical, evidence-based strategies.
What is Exercise Physiology?
Exercise physiology is the scientific study of how the body responds and adapts to physical activity. An exercise physiologist plays a key role in healthcare by assessing a person’s physical health, identifying limitations, and creating safe, effective exercise programs tailored to individual needs. They also monitor progress closely, making adjustments as required to ensure long-term results and safety. Unlike general fitness training, which often focuses on performance, weight loss, or strength goals, exercise physiology is evidence-based and medically guided, with a focus on improving health outcomes, managing chronic conditions, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Physiologically, exercise enhances cardiorespiratory endurance, muscle glucose uptake, endothelial function, and anti-inflammatory responses. These adaptations help control blood sugar, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall metabolic function.
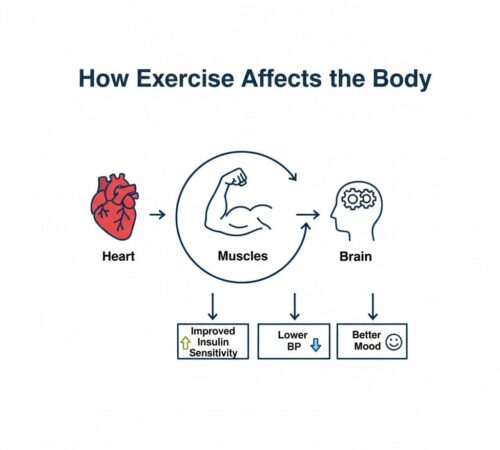
Why Exercise Matters in Chronic Conditions
Exercise is a powerful tool in managing chronic conditions because it supports the body in multiple ways. For heart health, it improves circulation and lowers blood pressure, reducing cardiovascular risks. In terms of metabolism, regular physical activity helps regulate blood sugar and supports weight management, especially important for diabetes and obesity. The musculoskeletal system also benefits through improved strength, mobility, and reduced pain, easing conditions like arthritis. Beyond the physical, exercise boosts mental health, lowering stress, depression, and anxiety. Backed by strong scientific evidence, consistent exercise enhances quality of life and even reduces hospital visits.
According to WHO, inadequate physical activity is one of the leading risk factors for non‐communicable chronic diseases; regular physical activity is estimated to reduce the risk of heart disease & stroke by ~19%, diabetes by ~17%, and depression/dementia by ~28-32%.
The Role of Exercise Physiology in Managing Specific Chronic Conditions
Exercise physiology plays a vital role in helping people manage different chronic conditions. By using science-based exercise programs tailored to an individual’s needs, exercise physiologists make physical activity safer and more effective. Below is a condition-wise breakdown:
1.Diabetes
Exercise physiology for diabetes management , Exercise helps people with diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity, lowering blood sugar naturally, controlling weight, reducing abdominal fat, and boosting energy and mood. Exercise physiologists design structured programs that combine aerobic activities like walking or cycling with resistance training. Blood sugar is monitored before and after exercise, and patients are educated on safely adjusting their exercise, meals, and medications. Recommended exercises include brisk walking or light jogging for 30 minutes, 5 times per week, bodyweight exercises like squats or modified push-ups 2–3 times per week, and yoga or stretching for flexibility.
Regular exercise can reduce HbA1c by up to 0.7%, similar to the effect of some diabetes medications (Journal of Diabetes Research, 2023).
2. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVD)
Exercise strengthens the heart, improves circulation, lowers blood pressure and cholesterol, reduces stress, and supports weight management. Exercise physiologists guide cardiac rehabilitation with gradual, safe exercise programs after a heart event, closely monitoring heart rate, oxygen levels, and effort. Programs start light and slowly progress to build endurance. Recommended exercises include walking outdoors or on a treadmill, stationary cycling or water aerobics, and light resistance training with bands or weights.

3. Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome
Exercise burns calories, reduces fat, preserves muscle, improves metabolism, and lowers the risk of related diseases. Exercise physiologists create personalized, lifestyle-friendly programs based on fitness and mobility and provide behavioral support to encourage sustainable habits. Recommended exercises include daily brisk walking or step goals, swimming or water walking, and strength training 2–3 times per week.
Exercise increases basal metabolic rate and helps preserve lean muscle, which improves long-term fat loss even at rest.
A 12-week supervised program can reduce body fat by 5–10% on average (Bloom Healthcare Study, 2025).
4. Arthritis & Musculoskeletal Conditions
Exercise keeps joints flexible, reduces stiffness and pain, strengthens supporting muscles, and improves mobility. Exercise physiologists focus on low-impact activities like water exercises, cycling, or yoga, combining strength and flexibility training while teaching pacing to manage pain. Recommended exercises include water aerobics or swimming, light resistance band exercises, and gentle yoga or tai chi.
additional tips :
- Warm up joints before activity
- Use low-impact tools (pool, stationary bike)
- Avoid high-load twisting movements
5. Cancer Rehabilitation
Exercise reduces fatigue, boosts energy, improves immunity and mental well-being, and helps patients regain independence after treatment. Exercise physiologists create gentle, tailored programs based on energy levels, focusing on daily functions and safe monitoring alongside medical treatment. Recommended exercises include short walks of 10–15 minutes, gradually increasing duration, breathing and relaxation exercises, and light resistance exercises using bands or bodyweight.
How Exercise Physiologists Personalize Treatment
1. Importance of Initial Health Assessment
The first step in working with an exercise physiologist is a thorough initial health assessment, which lays the foundation for a safe and effective exercise program. This assessment includes reviewing medical history, current medications, previous surgeries, and any relevant health concerns. Physical fitness testing evaluates strength, flexibility, endurance, and balance to determine current functional abilities, while lifestyle analysis examines daily activity levels, work demands, sleep patterns, and stress levels. Establishing this baseline ensures that exercise programs are tailored safely, reduce the risk of injury, and maximize effectiveness in managing chronic conditions.
2. Tailored Exercise Prescription (FITT Principle)
Based on the results of the initial assessment, exercise physiologists design personalized programs following the FITT framework, which helps ensure the right type and amount of exercise for each individual. The FITT principle considers frequency (how often sessions occur), intensity (effort level), type (aerobic, strength, flexibility, balance), and time/duration (length of each session). For example, a patient with diabetes may focus on moderate aerobic activity to control blood sugar and strength training to improve muscle mass and insulin sensitivity, while someone with arthritis may benefit more from low-impact aerobic exercises, gentle strength training, and mobility routines to reduce joint pain and stiffness.
3. Safety Protocols for High-Risk Patients
Risk management is essential when designing exercise programs for patients with chronic illnesses. Exercise physiologists often collaborate with doctors to obtain medical clearance and monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels during sessions. Exercises may be adapted to reduce risk, including using low-impact options or supervised training, and emergency preparedness is always considered to recognize warning signs of overexertion.
Common Warning Signs to Stop Exercise:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Dizziness or unusual fatigue
- Unexplained shortness of breath
5. Ongoing Progress Tracking & Adjustments
Exercise physiologists continuously monitor patient progress and adjust programs as health improves or new challenges arise. Measurable goals, such as improved stamina, reduced pain, or better glucose control, help track results, while motivation and education encourage long-term adherence. Exercise prescription is never static—it evolves with the patient to ensure ongoing effectiveness and safety.
Benefits of Working with an Exercise Physiologist
An exercise physiologist provides safe and evidence-based programs designed to suit individual health needs, making exercise both effective and risk-free.
With the right guidance, many people experience a reduced reliance on medications, as exercise helps control symptoms of conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
These programs also improve quality of life and independence, allowing individuals to move more freely, manage daily activities with ease, and feel stronger overall.
Most importantly, exercise physiologists offer education for long-term self-management, giving people the tools and confidence to stay healthy even outside of professional sessions.
You Can Also Read : How to Choose the Best Physiotherapist in Sydney for Your Specific Needs
Practical Tips for Patients
Start slowly with low-impact activities and gradually increase intensity. Consult an exercise physiologist or healthcare professional for a safe, personalized plan. Simple exercises like walking, stretching, or bodyweight movements done consistently, combined with a balanced diet, good sleep, and stress management, can effectively support chronic condition management.
When to Seek an Exercise Physiologist
Knowing when to seek the guidance of an exercise physiologist is crucial for managing chronic conditions safely and effectively. If you find yourself struggling with persistent symptoms despite taking prescribed medications, it may be time to consult a professional who can tailor an exercise plan to your needs. Additionally, if you are unsure how to exercise safely due to an existing condition, an exercise physiologist can provide guidance to prevent injury while improving your health. Those recovering from surgery or hospitalization can also greatly benefit, as specialized programs can help restore strength, mobility, and overall function under professional supervision.
You may also Read : 5 Signs You Should See a Physiotherapist in Sydney Before It Gets Worse
Conclusion
Exercise physiology offers a powerful, evidence-based way to manage chronic conditions and improve overall wellbeing. By combining personalised exercise programs with professional guidance, it helps enhance heart health, mobility, strength, and mental resilience.
At The Movement Mill, our experienced team provides tailored care to support individuals across Sydney, helping them move confidently and live pain-free. Whether you’re managing diabetes, arthritis, or recovering from injury, our exercise physiologists ensure every program fits your unique goals and lifestyle.
Take control of your health today — start your journey with The Movement Mill in Sydney and experience the difference movement can make.
FAQs
What makes exercise physiology different from physiotherapy?
Exercise physiology focuses on chronic condition management through exercise prescription, while physiotherapy targets rehabilitation after injury or surgery.
Can I exercise if I’m on medication?
Yes, but under supervision — exercise physiologists coordinate with your doctor to adjust your plan safely.
How long before I notice improvements?
Most clients see noticeable results — better stamina, lower BP, improved glucose — within 6–8 weeks of consistent adherence.
Is telehealth exercise physiology effective?
Yes, studies show remote monitoring and virtual sessions can maintain adherence and deliver similar outcomes.

